Parasites have zoological and ecological classifications.
zoologicalTaxonomy determines that parasites belong to certain systematic categories: type, class, order, family, genus.
environmentalClassification is based on characteristics of the parasite's lifestyle.
- specific parasites.Parasitic on only one animal (pinworms, dwarf tapeworms, lice);
- nonspecific parasites- Parasitic on different types of animals (mosquitoes, tapeworms, trichinella).
Depending on the localization of the parasite in the host organism:
External parasites-Parasitic on the outer skin of the host (blood-sucking arthropods);
Internal parasites- Habitat is the host organism:
- in abdominal organs related to the external environment (digestive, respiratory and genitourinary systems) - roundworms, paragonimiasis;
- in tissues (musculoskeletal system, subcutaneous fat) - dracunculiae, Trichinella;
- intracellular (Plasmodium malaria);
transitional form.For example, in the stratum corneum of the epidermis, itching parasites, which breathe oxygen from the atmosphere.
Depending on how closely the parasite's developmental cycle is linked to the host organism:
- permanent parasite- the entire development cycle takes place in one owner's body (trichomoniasis, scabies, lice);
- temporary parasite- Only part of the developmental cycle occurs in the host organism (blood-sucking insects, worms).
Based on the number of hosts that change periodically during the development cycle:
Hosts are living organisms that parasites use as a source of food and habitat.
Host classification
The host is divided intofinal, intermediateandreservoir.
final (basic, definitive)- The parasite is in a sexually mature stage in its body or as a host for sexual reproduction (Anopheles mosquitoes for Plasmodium, and humans for sexually mature pork tapeworms).
Middle- A host in which the parasite is in the larval stage or asexual reproduction (in humans with Plasmodium malaria; in pigs, in wild boars with tapeworms).
reservoir- An organism that is not an essential host in the life cycle of the parasite, but once entered the parasite does not die, although it is not further developed. Parasites accumulate in reservoir hosts. When the host is eaten by the final host, the parasite completes development in its body. In the human gut, for example, a broad tapeworm can parasitize. Man is his ultimate master. The developmental cycle has two intermediate hosts: the first is a one-eyed crustacean, and the second is a variety of fish. But non-predatory fish can be eaten by predatory fish, such as barracuda. In this case, the worm larvae did not die, but instead accumulated in the barracuda's muscles and became the host.
so,The host organism is a kind of habitat for the parasite.The doctrine of host organisms as parasite habitat was most fully developed by Academician E. N. Pavlovsky.The sum of all organisms living in any organism at the same time is called a parasitic disease.
Parasite taxonomy
Depending on how necessary the species is to live a parasitic lifestyle:
- Pseudoparasitism- Individuals of one free-living species accidentally enter the body of another species, where they still survive and interfere with the normal life of the host. After a brief parasitism in the host organism, pseudoparasites die or are released into the environment. For example, coprophagous amoeba can live in feces. When stools dry out, they can form cysts. Cysts of the coprophagous amoeba may accidentally enter the human gut. Usually cysts pass through the intestines and are excreted into the external environment with feces. In some cases, amoeba in the human gut emerge from cysts and parasitize within a short period of time, resulting in acute digestive disorders.
- facultative parasitismIndicates that a species has the potential to lead a free and parasitic lifestyle. With this form of parasitism, a free-living species accidentally enters the body of another species, temporarily using it as a habitat and food source. Compared to pseudoparasites, facultative parasites remain in the host organism for longer periods of time. An example of facultative parasitism is the free-living amoeba of the genusNegriliaandAcanthamoeba. Negleria and Acanthamoeba live in bodies of water that receive sewage. Entering the body through oral or skin wounds can cause severe, sometimes fatal, amebic meningoencephalitis.
- true (obligate) parasitism- A parasitic lifestyle is mandatory for at least one developmental stage. True parasites are trypanosomes, Leishmania, Plasmodium, porcine and bovine tapeworms, roundworms and many others.
According to the localization of the parasite in the (top) host organism:
- External parasitesLive on the host's body surface and feed on blood (hemophagocytic cells) or the stratum corneum and its derivatives (corneal phages). Human ectoparasites are usually insects and mites. Ectoparasites are often also specific carriers of human pathogens.
- Parasites that live in host cells, tissues and cavities are calledInternal parasites. Thus, localization distinguishes intracellular, tissue and coelomic parasites. Endoparasites can affect any organ. There are intestinal parasites (bandworms and roundworms, protozoa), liver parasites (flukes), lung parasites (paragonimiasis), genitourinary system (schistosomiasis, trichomoniasis) and other organs. The parasite can localize to only one organ or to infect multiple organs of the host.
Depending on when the parasitic species is in contact with the host:
- temporary parasiteThey usually live on the outer skin of the host (ectoparasites). They are only connected to the host organism through the food chain (such as hemophagocytic cells), and the contact time with the host is much shorter than that of free-living.
- Fixed parasitesSpend a long time with the owner, sometimes their whole life. For quiescent parasites, the host organism is not only a source of food, but also a habitat. Fixed parasites include almost all endoparasites and some ectoparasites. Fixed parasitics include two forms of parasitics:periodic(parasites spend part of their lives in the external environment) andcontinuous(The parasite does not leave its host). Periodic parasitism is more common in nature than permanent parasitism.
by specificityParasites are divided into monospecific and multispecific.
- Parasites that live in organisms adapted to different host organism species are calledmultispecificA variant of polyspecificity is polyphagia - the ability of blood-sucking parasites to feed on the blood of hosts of different species. For example, the sexual maturity stage of liver flukes (Fasciola hepatica) parasitic on a variety of herbivores; many types of mosquitoes (familyCatfish) feed on the blood of hosts belonging to various mammalian species.
- If the parasite adapts to the life of a certain host, it isMonospecificA variant of monospecificity is monophagy - feeding blood-sucking parasites at the expense of a host of the same species. An example of monospecificity is the human louse parasitizing the specieshuman lice. Once on the body surface of any other species, these lice die. Human Ascaris (roundworms) are also monospecific parasites. Once inside the body of another host, they die before puberty.
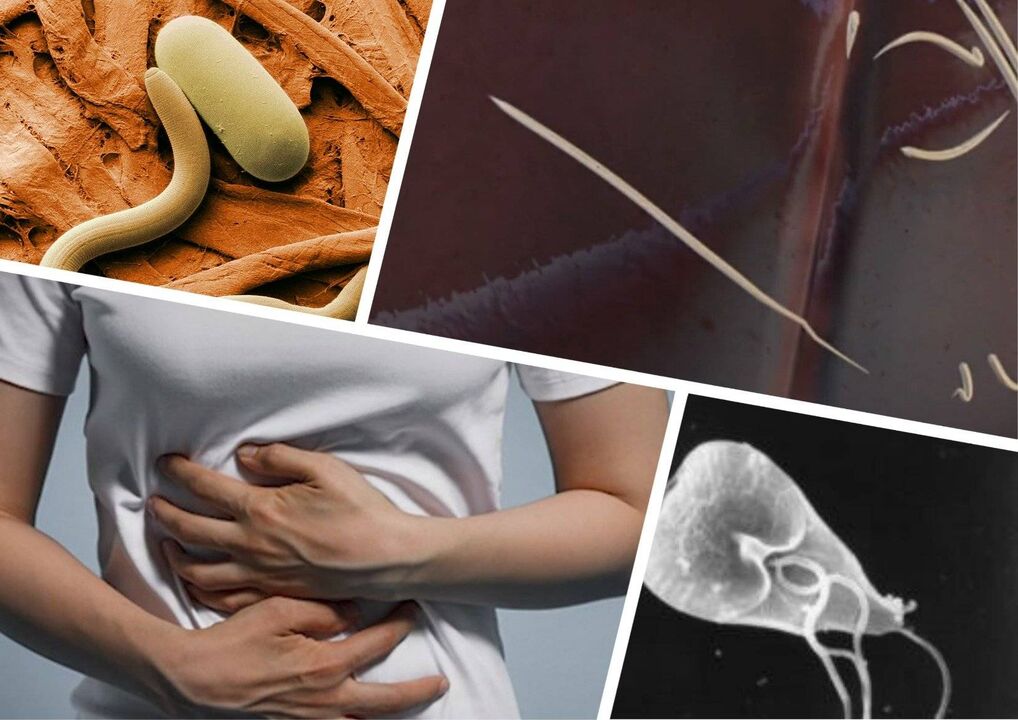
What parasites are in the human body
The flora in the human body is an excellent environment for microorganisms belonging to the pathogenic flora to inhabit and reproduce actively. The types of parasites in the human body are generally divided into two options - those that are imperceptible and have little effect on overall health, and those that are potentially harmful. During their lifetime, they are capable of not only negatively affecting organs, but also releasing toxic substances that poison all living things.
Most parasites in humans are nematode worms, diagnosed in both adults and children. Parasites can vary in their location (in the gut, liver, heart and even in the brain), size, life cycle and even their time in the body.
The most common types of parasites that affect humans - nematodes are as follows.
The microbe lives in the lining of the large intestine while spreading the eggs of its future offspring outside the large or small intestine, such as on bed sheets. Mostly, this parasite is diagnosed in children. Worms cause anal itching, decreased appetite, sleep grinding and fatigue.
The life cycle of microorganisms is about one month, and they reach a size of 12 mm. Pinworms are very resistant to the external environment, and new species emerge 6 hours after spawning.
These worms live in cats and dogs and enter the internal environment of humans through contact with these animals. These intestinal parasites can grow up to 3 cm in length and can be found in all internal organs and blood vessels without going outside.
They are among the most dangerous types of infectious parasites to humans. Grows up to 3 cm long and can live a very long cycle. They penetrate all organs of the system while actively multiplying.
Trichinella
Invasion of parasites caused by Trichinella can lead to negative consequences: edema, fever, dermatitis, indigestion and various allergies, including food. The main difficulty in detecting these worms is their microscopic size, which is usually no more than 4 mm. Worms living in the gut are able to penetrate blood vessels through which it travels through the bloodstream throughout the body and settles in any organ.
Trematodes also frequently live in the human gastrointestinal tract. They are characterized by a flat shape and the presence of suction cups. These extra organs are necessary for them to stick to human organs in order to suck useful substances out of them.
The classification of parasites according to helminth type includes a class of flukes, consisting of the following microorganisms:
- Opisthorchis is a simple parasite that normally lives in the stomach, gallbladder, pancreas and liver, causing the development of gastritis, ulcers and pancreatitis. He has no interest in internal organs of any kind.
- Strongyloides - Enterocomedone, is a worm up to 2 cm long. It can affect the gastrointestinal tract. He did not live long, but at the same time, his activities led to diseases such as asthma, gastrointestinal dysfunction, bronchitis, weakness, etc.
Because flukes can enter any human organ and tissue, their invasion is considered the most common and the most difficult to treat.
These microbes devour large amounts of tissue and blood, often incapacitating the circulatory system.
Of all the existing parasites that live in humans, the most dangerous are the tapeworms. The length of this worm can reach 10m. Thinking about what kind of parasites live in the human body, it is difficult to imagine that such a huge worm can fit into the human body. They mostly got indoors while consuming contaminated meat.
The most common types of tapeworms are:
- Pork tapeworm - grows up to 8 m long, initially without symptoms of invasion, but later pork tapeworm activity causes intestinal obstruction. It is also possible to develop weakness;
- Bovine tapeworm - can grow up to 18 m long. It causes dangerous diseases in humans, including anemia, intestinal obstruction, allergies, gastrointestinal disorders, and thus the nervous system;
- Broad tapeworm - this parasite reaches a length of 8 m. One of the few human parasites that live in the small intestine. lead to anemia, weakness, digestive problems and intestinal blockage;
- Echinococcus - Considered the most dangerous tapeworm, infection does not show any symptoms in the first stage. However, the rapid spread of worms throughout the body can lead to tumor formation.
protozoa
Think about what kind of parasites there are in the human body, and don't forget the possibility of infecting so-called protozoa. This type of microbe is not related to the three types of worms, as it constitutes its own special parasitic species, living in various human organs.
Protozoa belong to a class of endoparasites that can be located in almost any corner of the body. The species is named for its simple structure consisting of only one cell. However, they can cause various dangerous diseases in the human body.
Main types of parasitic protozoa:
- Trichomonas. Despite having only one cell, their structure is very complex. There are several types of this type of parasite, depending on the degree of localization: oral, intestinal and vaginal. The most common infection when this organism is present in the reproductive system. Trichomonas often causes prostatitis in men. affect the brain and nervous system;
- Lambia. localized in the intestine. They can cause dysbiosis, gastrointestinal upset and systemic toxicity. Usually attached to the mucous membrane of the duodenum, where they multiply actively;
- amoeba. Can cause weakness and indigestion, and can cause intestinal obstruction;
- Toxoplasma. This parasite is very dangerous for pregnant women as it can cause miscarriage in the early stages. Additionally, Toxoplasma can cause eye, nervous system and heart disease.
A particular danger of protozoan unicellular microorganisms infecting humans is that, in most cases, developing infections are asymptomatic.
External parasites
Parasitic microorganisms of this type, such as ectoparasites, constitute a separate group of dangerous infection carriers. This class is distinguished by the fact that their representatives are located only on the surface of the human skin, but despite this, they are capable of contracting dangerous diseases such as anthrax, typhoid, encephalitis, trypanosomiasis, etc.
It is not difficult to identify the appearance of this group of parasites, as usually they cause noticeable discomfort to the host. The main consequences of their bites include allergic reactions, itching and burning.
This microorganism can only be dealt with by means of special means. In addition, sanitation of premises, bed linen and clothing is often required. Very dangerous alien species of ectoparasites that can be picked up while traveling. The bites of some of them can be fatal.
Read more: Is it possible to treat a nursing mother's throat with the help of Lugol? Will it hurt the chest?
The fight against parasites in the human body, regardless of their location, should be done comprehensively in consultation with a doctor. However, it is important to correctly diagnose dangerous microbial infections.
Typically, the symptoms of a person's susceptibility to a parasitic infection are as follows:
- Constipation - due to intestinal obstruction associated with large sized worms. In addition, worms can block the flow of bile, causing pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- Frequent gas formation - usually caused by worms that colonize the small intestine. This also includes so-called irritable bowel syndrome;
- Diarrhea - Liquefaction of feces is caused by special substances secreted by certain microorganisms. Too frequent loose stools may indicate infection;
- Allergic reaction - usually occurs on the waste products of microorganisms in the body. Eczema and rash may also occur;
- Joint and muscle pain and discomfort. If this sign appears for no apparent reason, you must check for the presence of parasites. Some of them prefer to live only in joint fluid and muscles, and pain is an immune response to the emergence of microbes;
- Weight gain, appetite problems - associated with poisoning of the body by the excrement of parasites and lack of glucose;
- Chronic fatigue syndrome, sleep disturbance, anxiety and irritability. He often said that the body's resources were exhausted due to the vigorous activity of parasites in the body.
There are many types of parasites that can live in the human body. Most early infections are completely asymptomatic. However, early treatment of parasitic infestation is considered the most effective and easiest.
What kinds of parasites live in the human body
Organisms that live in animals, humans, birds and fish and feed on their hosts are called parasites.The life activity of this organism in the human body does not bring any benefit, and the parasite can cause serious complications and even death. Consider the types of parasites in the human body in more detail. Below is a detailed breakdown of the parasites.
Variety
- The simplest - including Giardia, dysentery amoeba, trypanosomes, etc.
- Ascaris – roundworms and pinworms take root in the human body
- Flatworms - The human body is an excellent habitat for pork and cattle tapeworms, liver flukes, and more.
- Lice and Fleas
- Ticks and Gadflies
It is very difficult to deal with this type of parasite, because during their life they reliably settle down and attach to the walls of their organs with the help of special suckers and hooks.
Some can usually live in cells and tissues, from where it's nearly impossible to get them out. It's about worms. For insects, the situation is simpler, as they are usually located on the surface of the body and can be detected and destroyed in time.
Which parasites live in the gut? So, let's analyze each of their species and where the parasitic worms and protozoa live.
flatworm
This parasite is also very dangerous in the human body. These worms are called flatworms because their body shape resembles a flat ribbon. There is also a type of flatworm that is least harmful to humans - these are ciliates. But let's talk more about dangerous parasites -- flukes and tapeworms.
The flatworms of this species are small in size, but because of their suckers, they are very firmly attached to the walls of human organs. The flukes live primarily in the liver and intestines, causing anemia, persistent headaches and sudden weight loss. During its life, the worm invades the lungs and even the brain, with serious consequences. The sources of flukes are dirty water and plants.
This worm is very large in length and will constantly reach its full potential. A tapeworm can grow up to 6. 5 meters in its lifetime. The representatives of the tapeworms—bovine tapeworms and pork tapeworms—can reach lengths of up to 10 meters. Parasites live in the human gut, i. e. in thin places. The most dangerous tapeworm is Echinococcus, which affects the brain and lungs.
A normal appetite and weight loss are the main signs of a tapeworm infection.
roundworms
These types mainly occur in children - kindergarteners and elementary school students. The most popular are roundworms, which are pinworms and roundworms, both of which tend to live in the gut.
These types of parasites do not attach to the walls of human organs in any way because roundworms have no adaptations for this, but they are not easily removed. Pinworms tend to lay their eggs in the anal folds, causing unbearable itching in the perianal area. The children infect themselves "in a circle" - scratching the itch, pinworm larvae remain on the hands and under the nails, and the infection reoccurs when the children accidentally put their fingers in their mouths.
And if symptoms occur occasionally, people in the modern rhythm of life simply don't notice them or don't take them seriously. And very futile. There are many dire and irreversible consequences.
Experts recommend testing for parasites -- feces, blood -- at least once a year. After all, timely detection of parasites in humans and effective treatment will ensure further quality of life.
What happens to people with long-term survival of internal parasites?
- As the parasite reproduces and grows, the power runs out.
- Immunity is greatly reduced because the body puts all its power into pest control.
- Any, even the simplest virus or infection can infect a person because the body cannot protect itself from the virus.
- During their life, parasite individuals secrete toxins that gradually accumulate in the human body. It is gradually poisoned and filled with various infectious and even malignant diseases.
prevention
Prevention is an important part of pest control. What are the parasites in the human body. As for worms and protozoa, modern medicine offers a large selection of medicines for pest control.
But you should not prescribe it yourself, you must consult a specialist first, especially if you are concerned about any symptoms. After performing the necessary tests, the doctor himself will prescribe the appropriate medication depending on how the parasite is living in the body.
After all, every drug acts on certain types of parasites; unfortunately, there is no universal one yet. An expert will help you choose a drug related to this condition to fight a certain parasite in your body.










